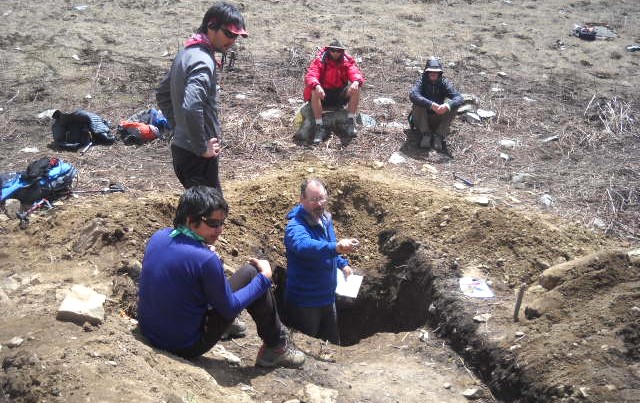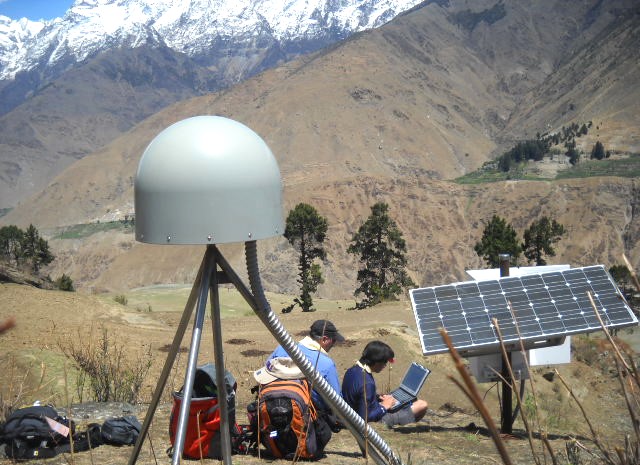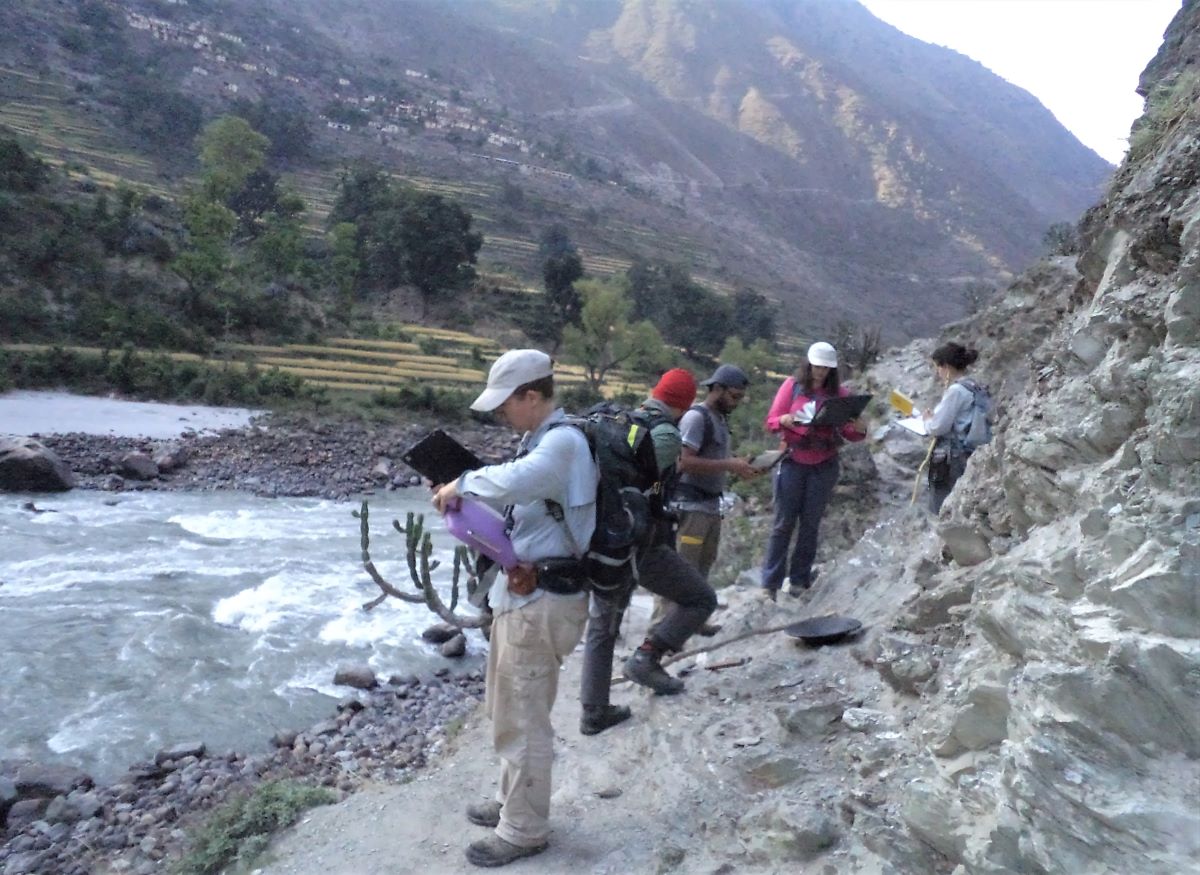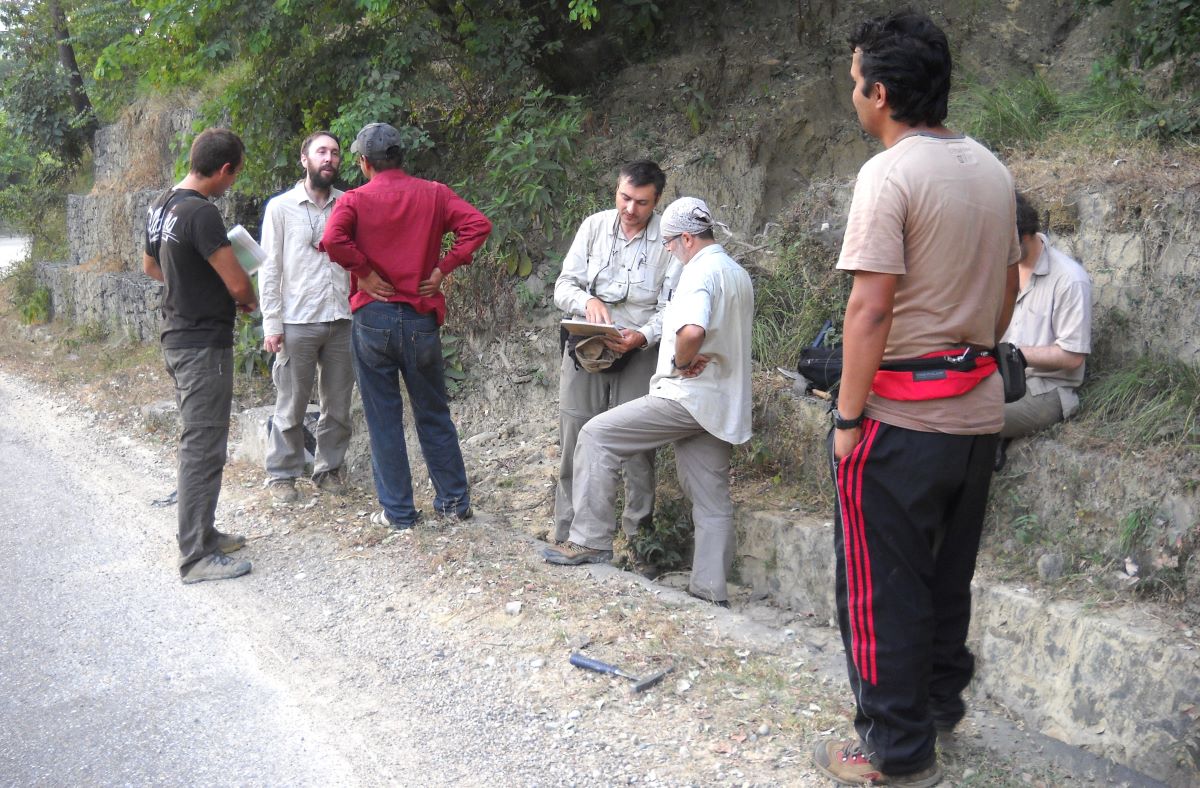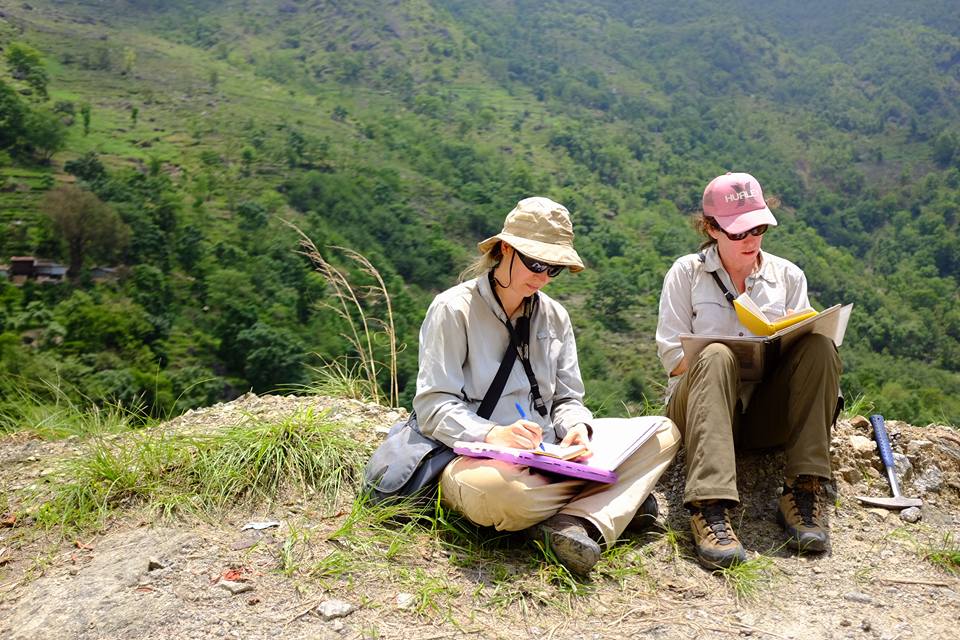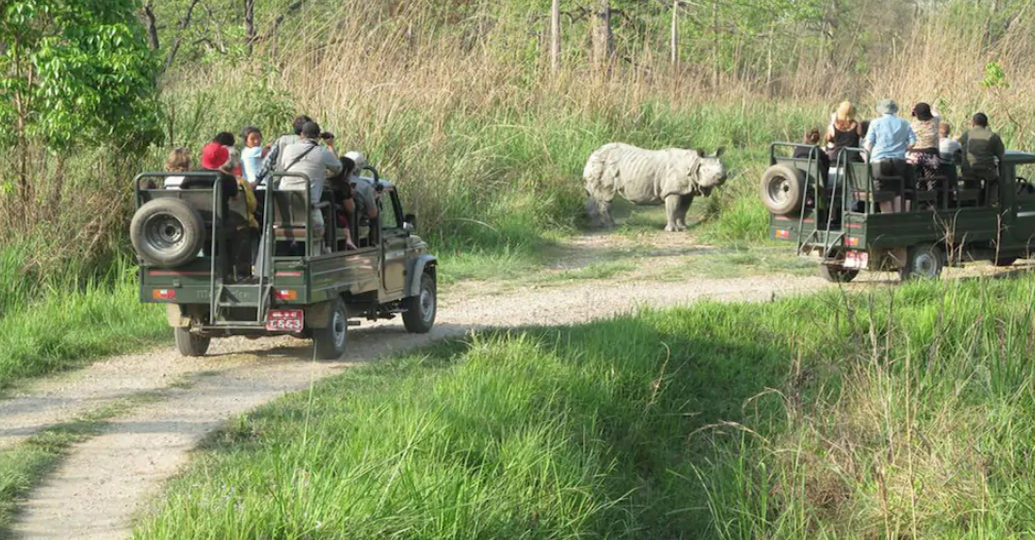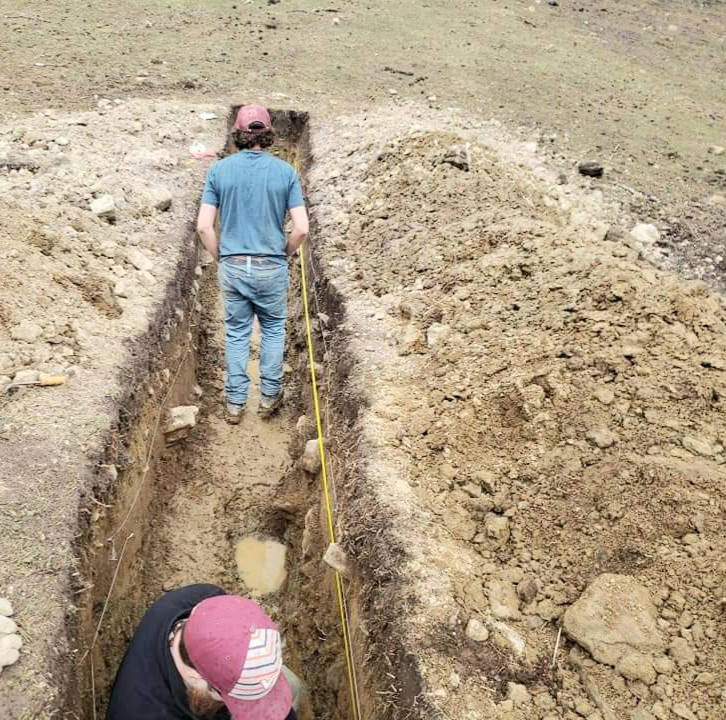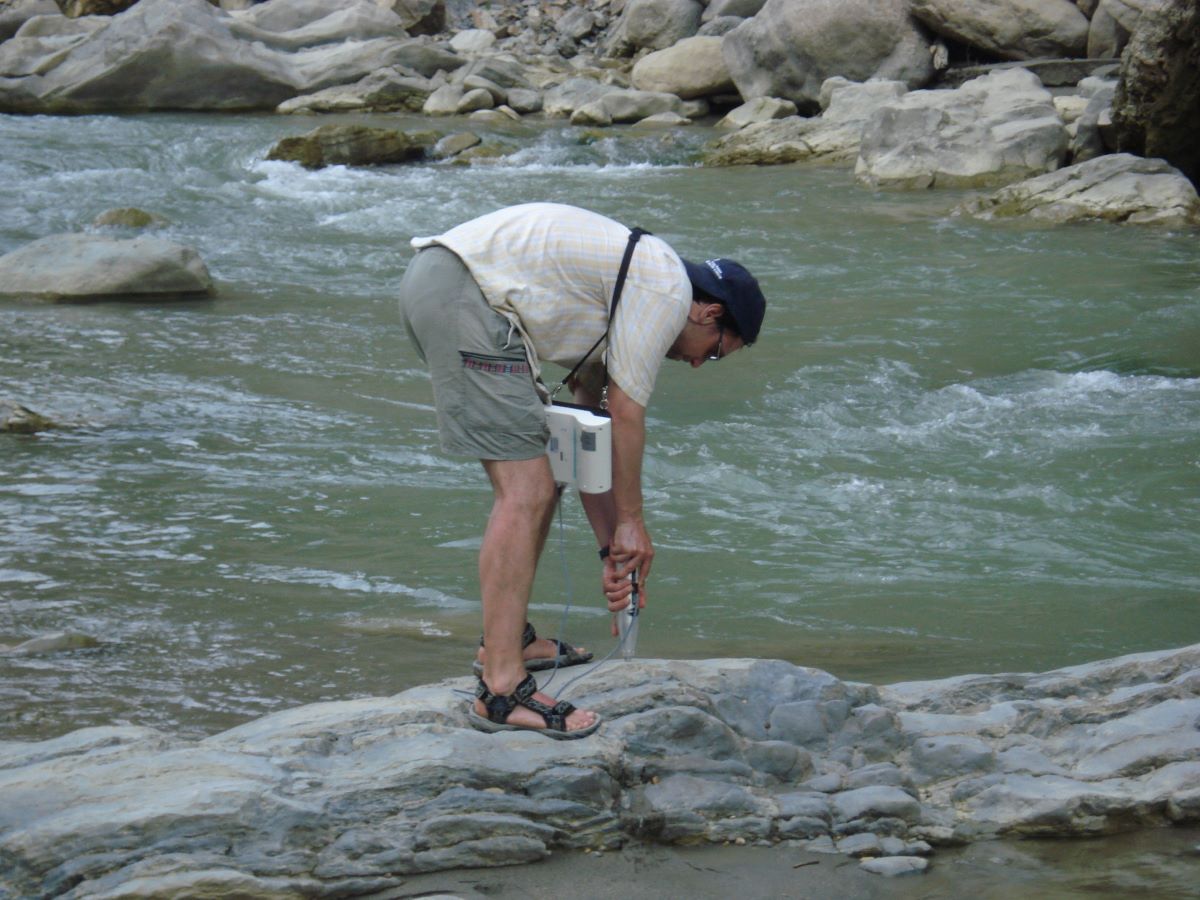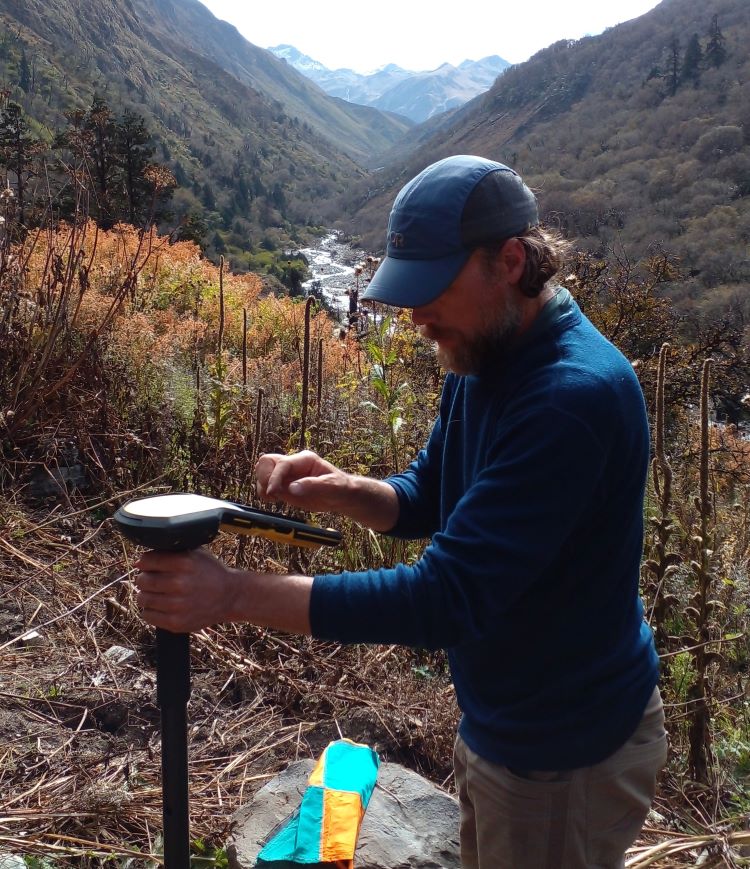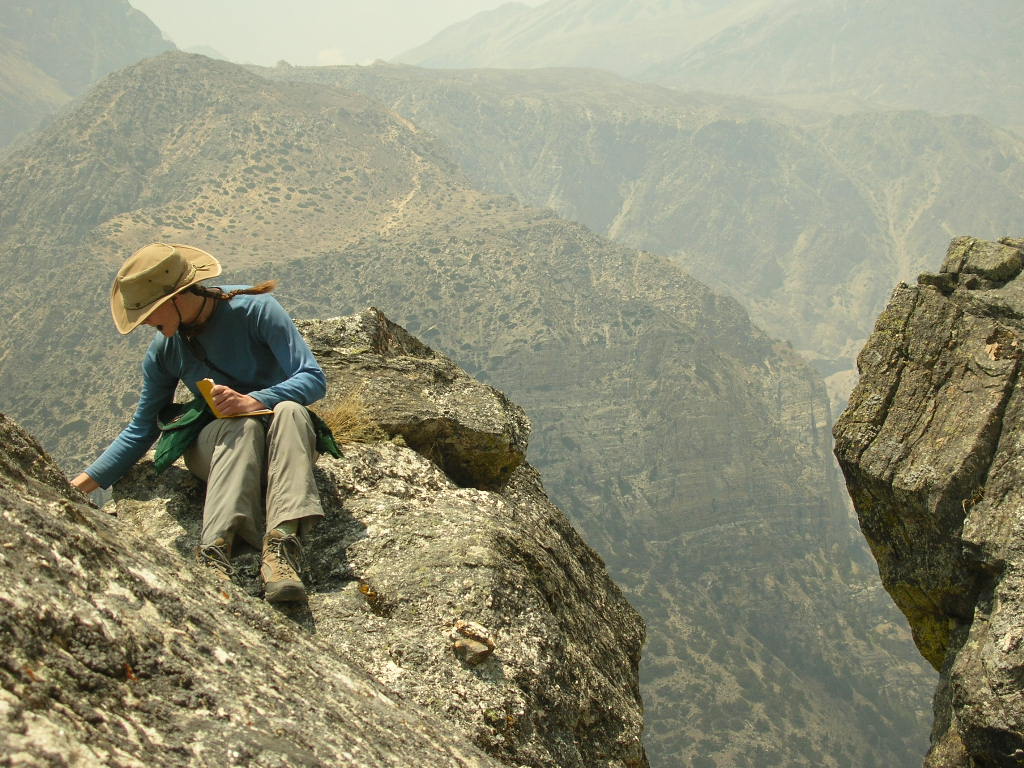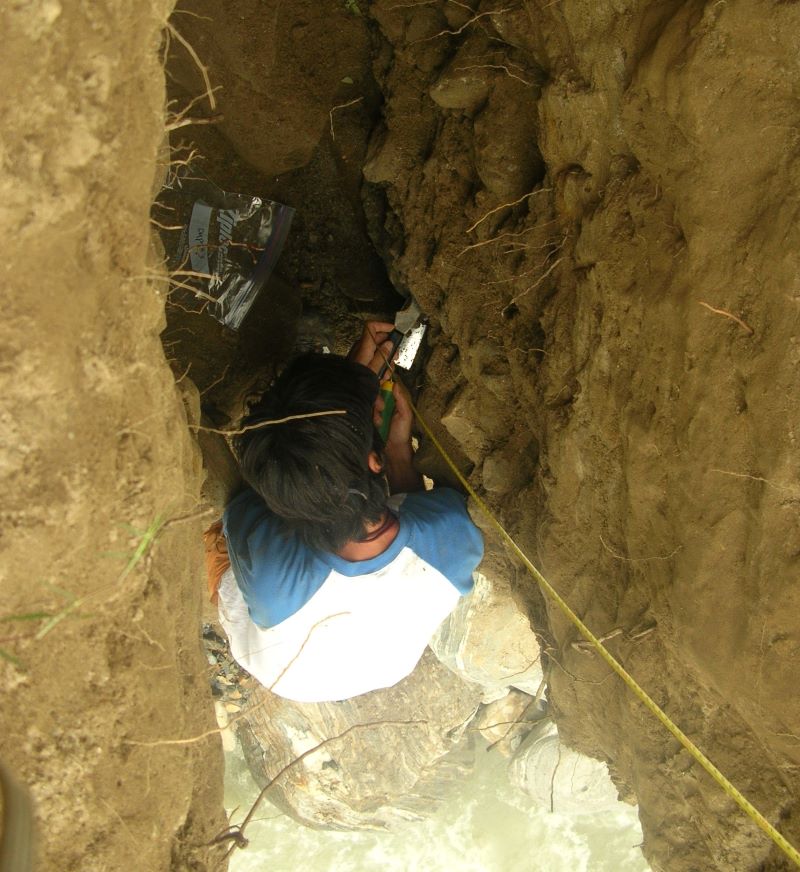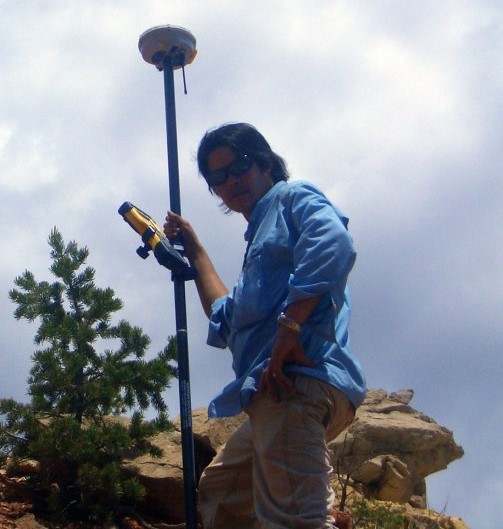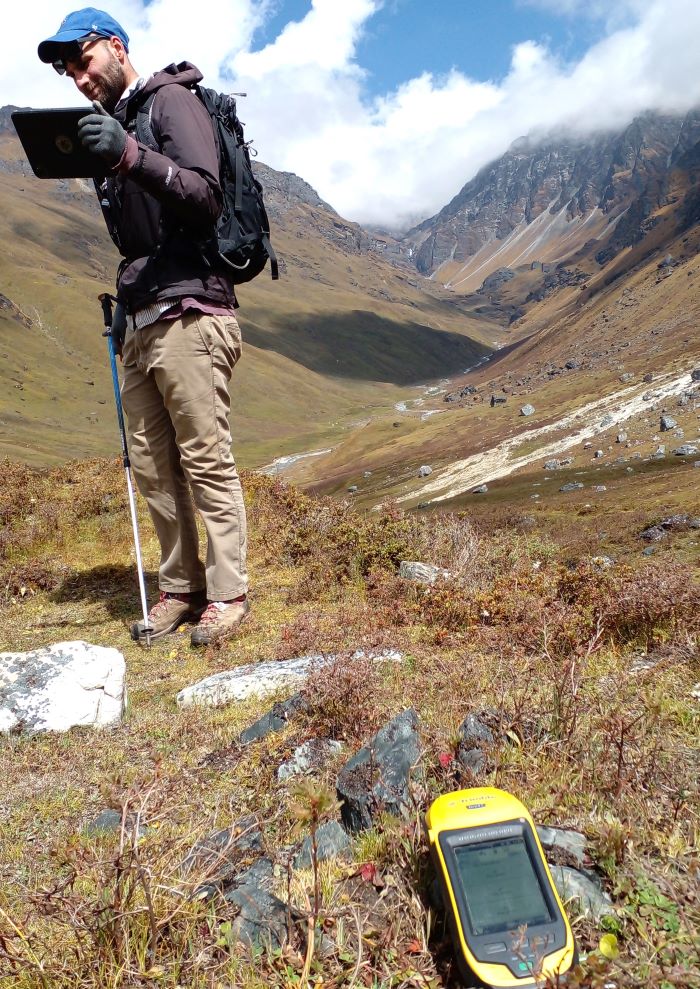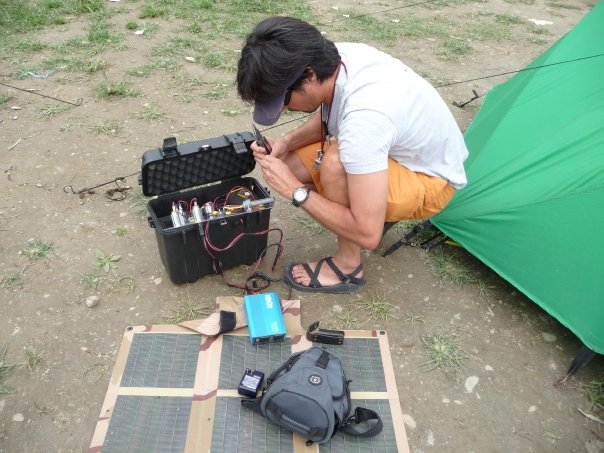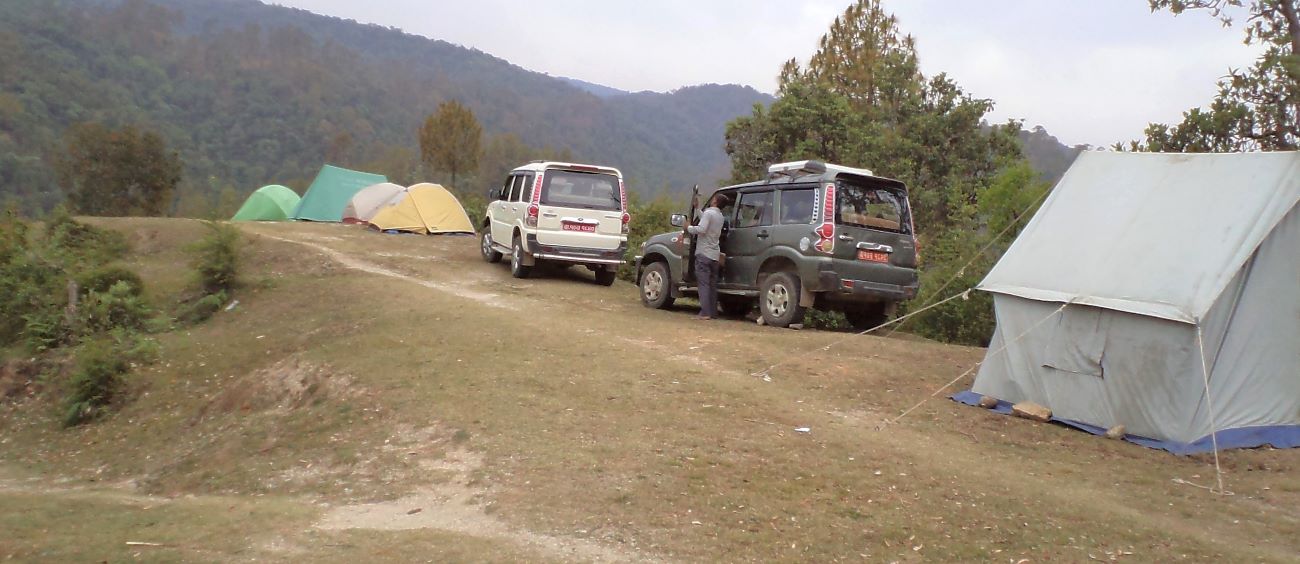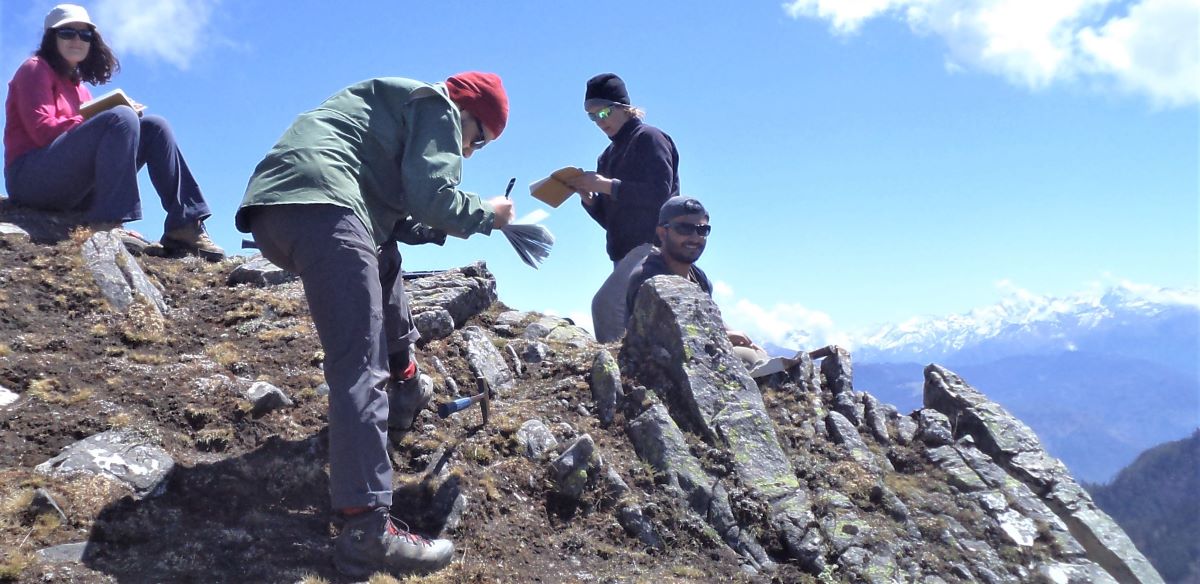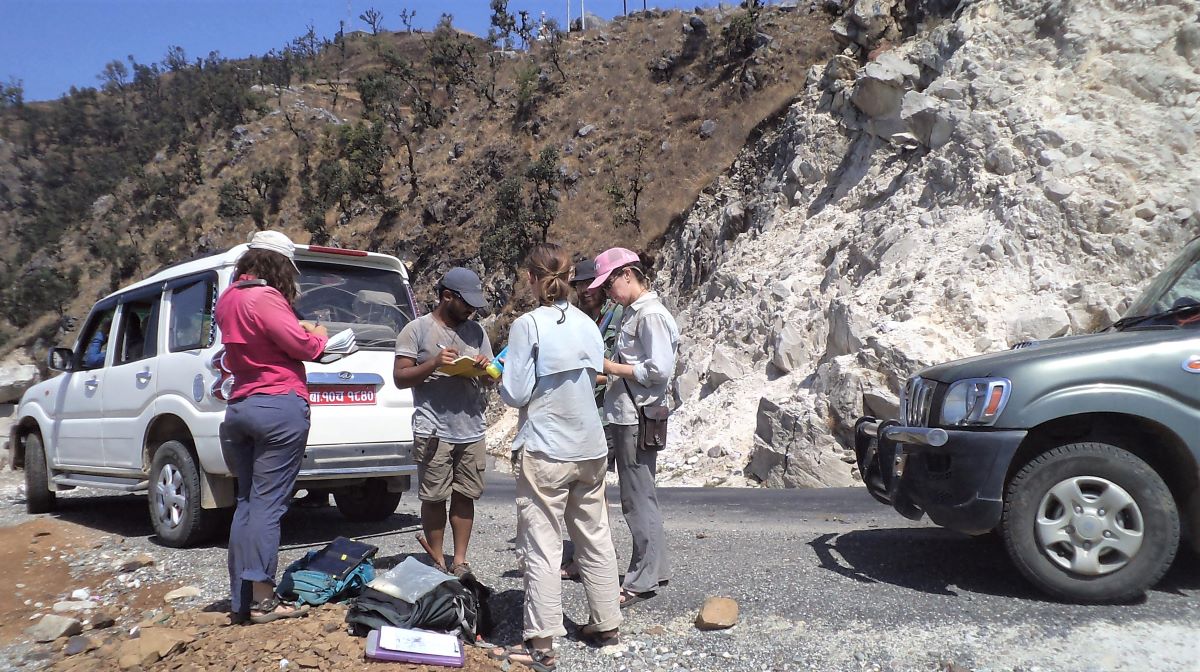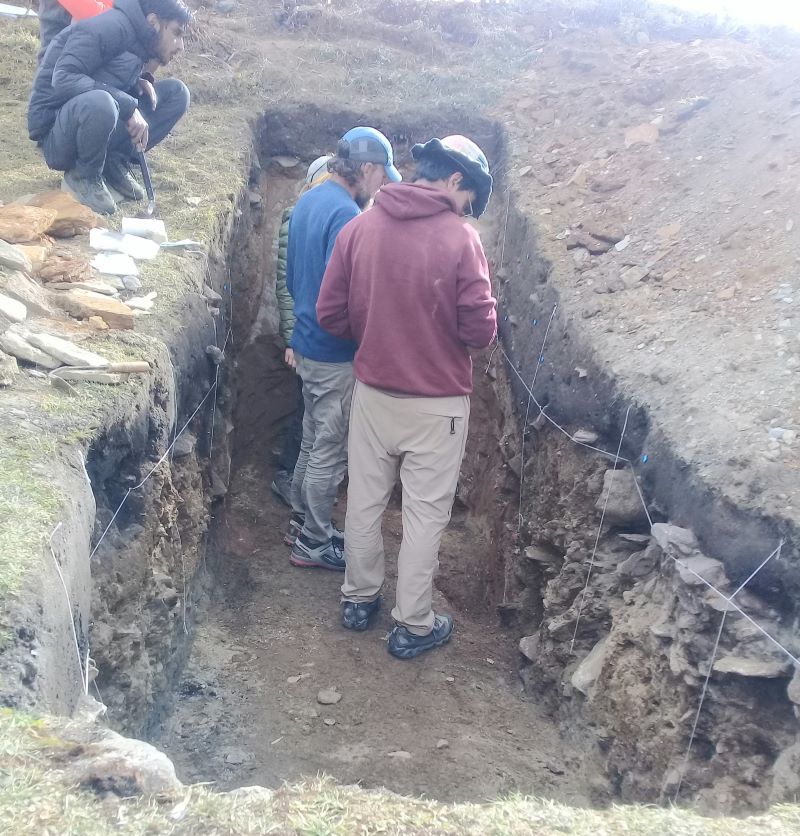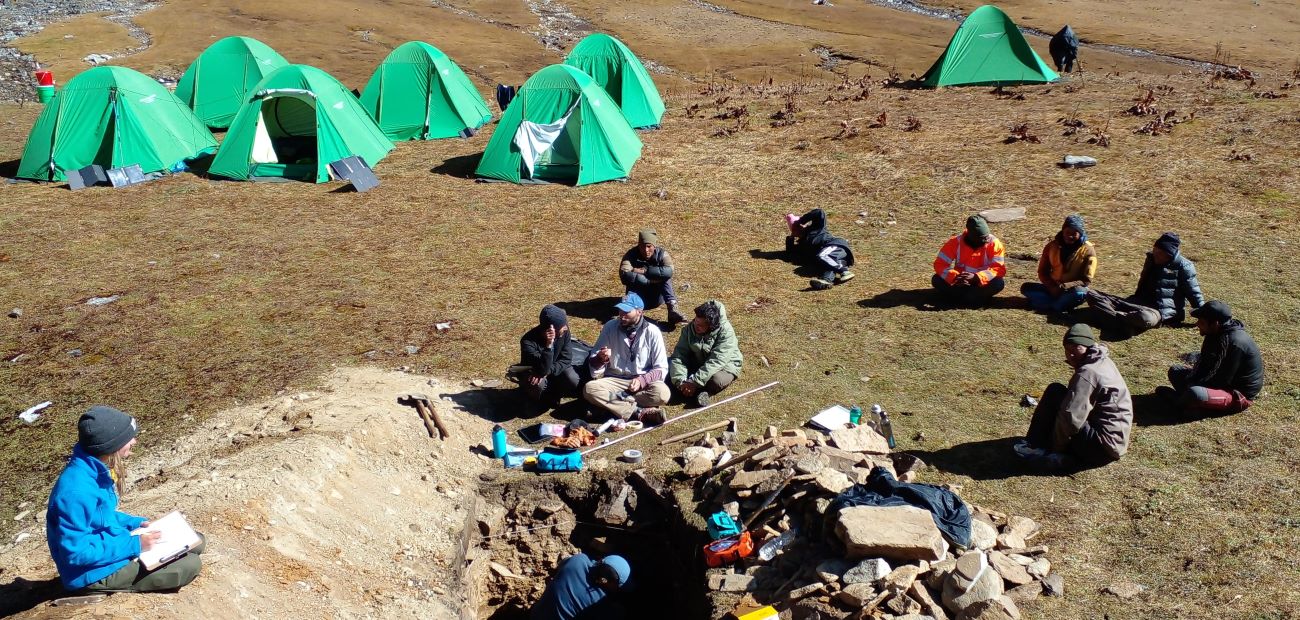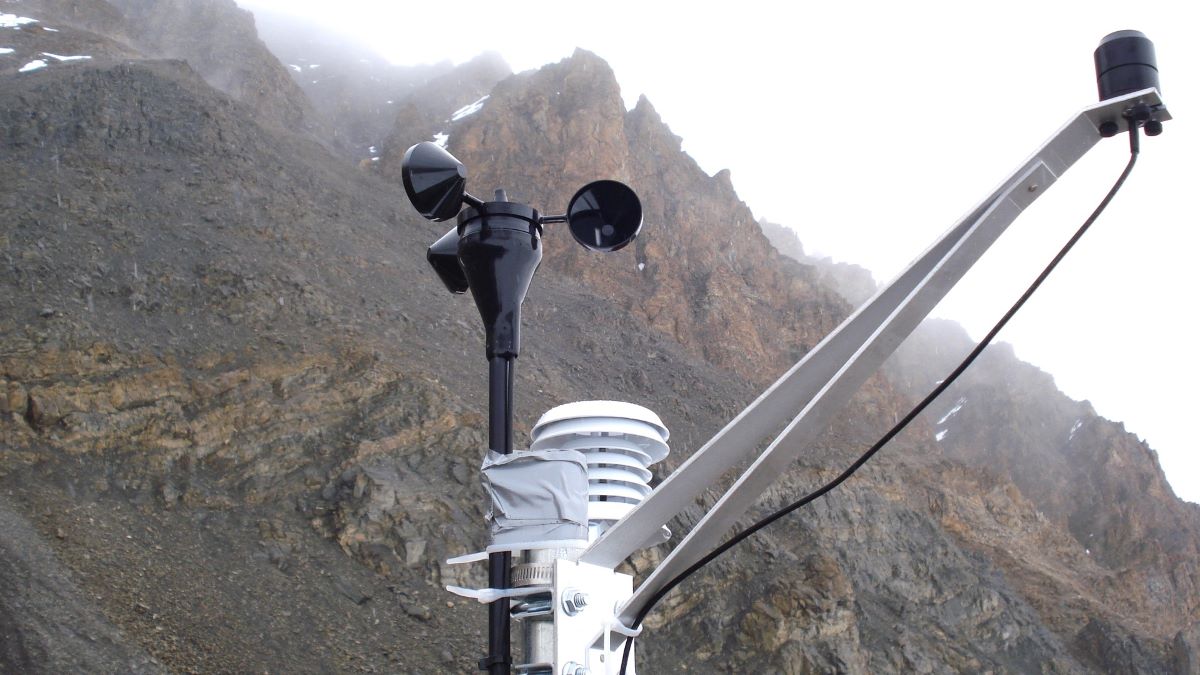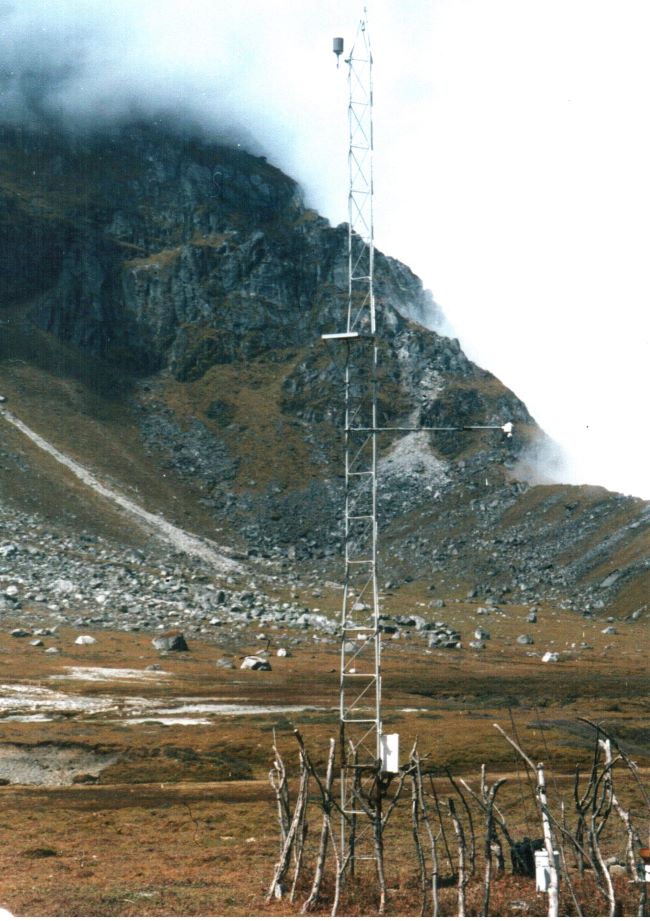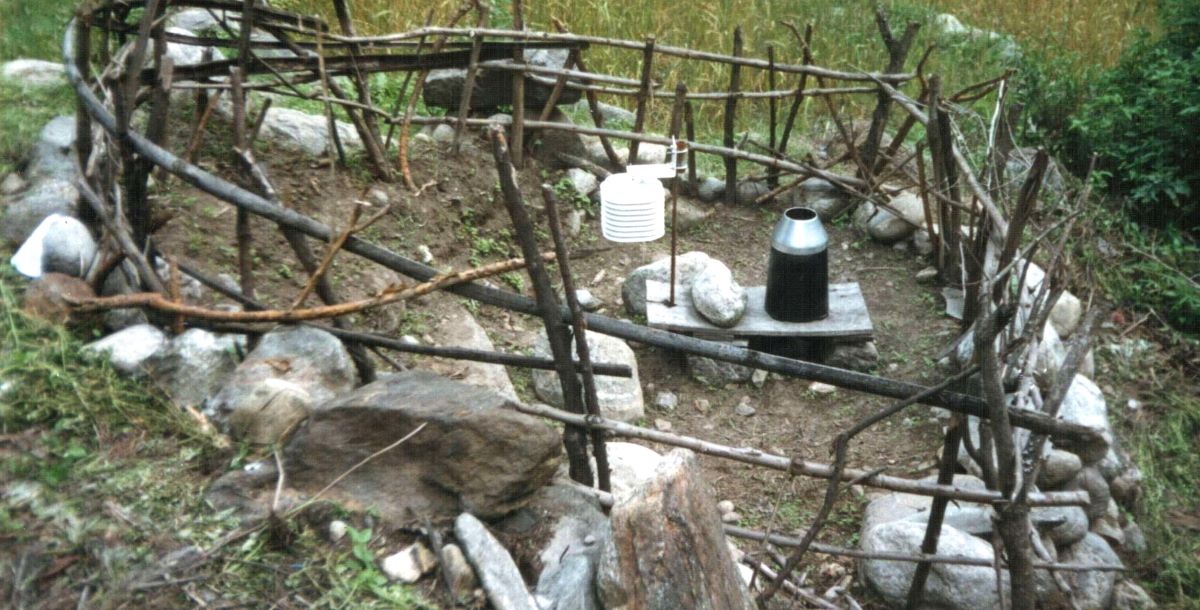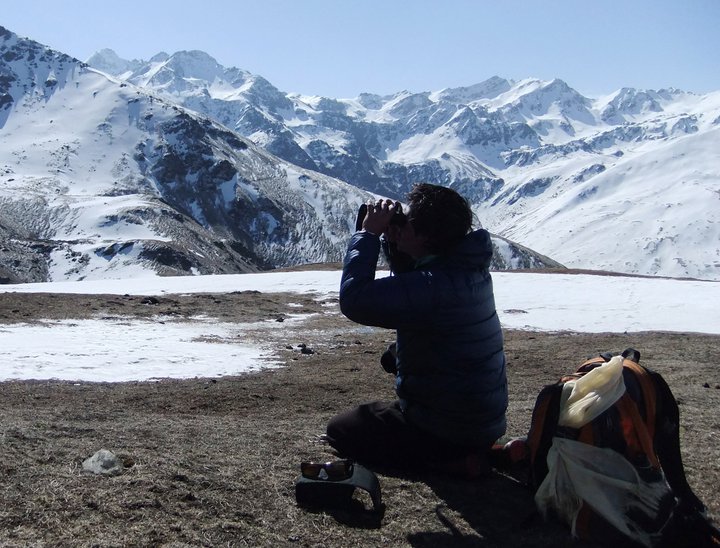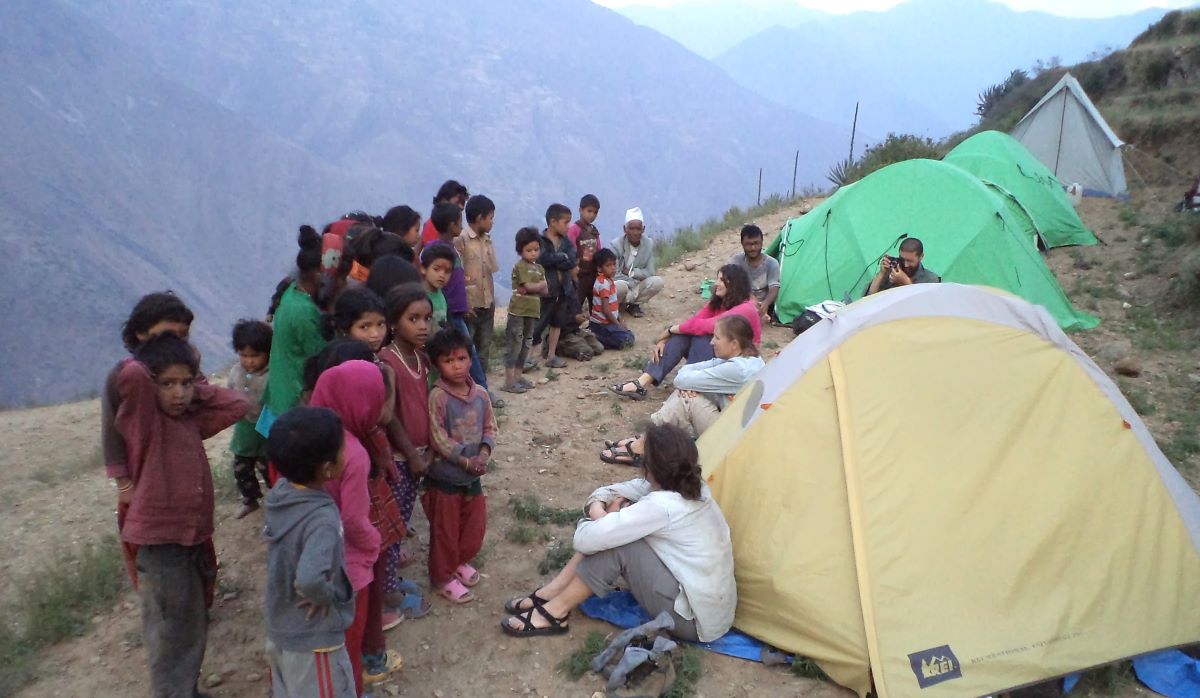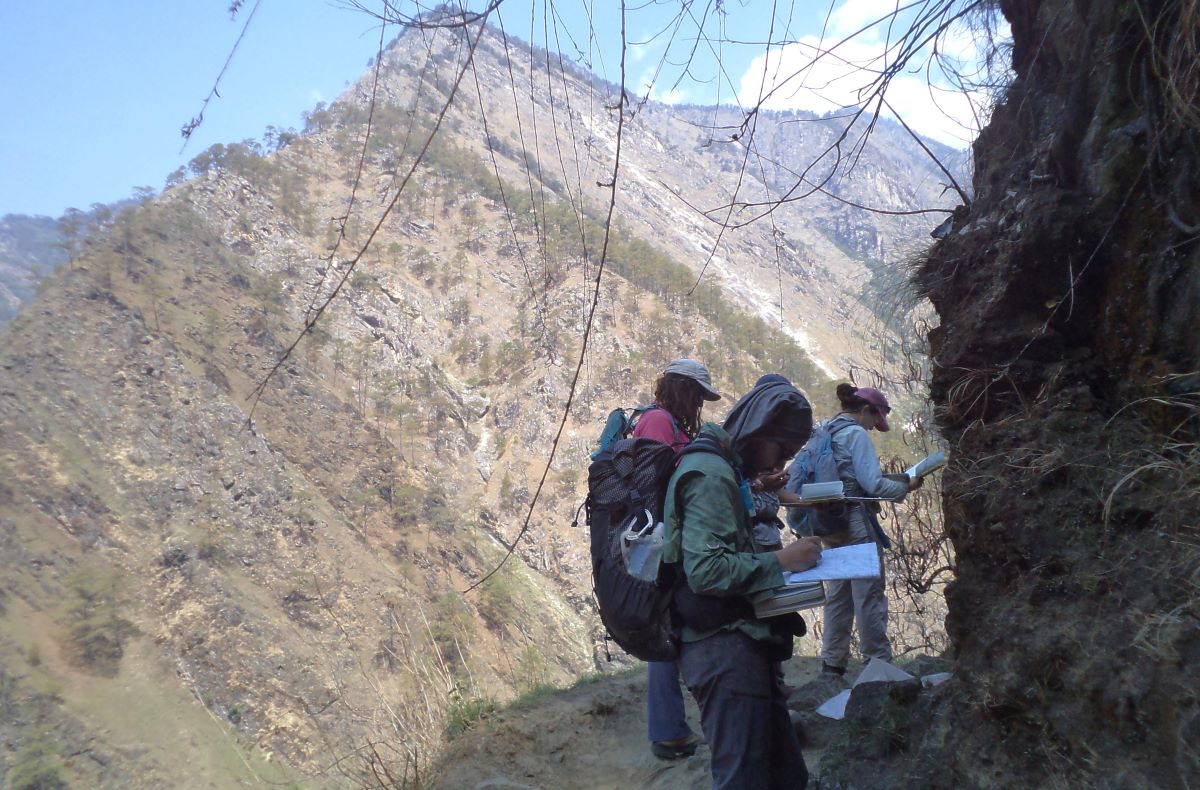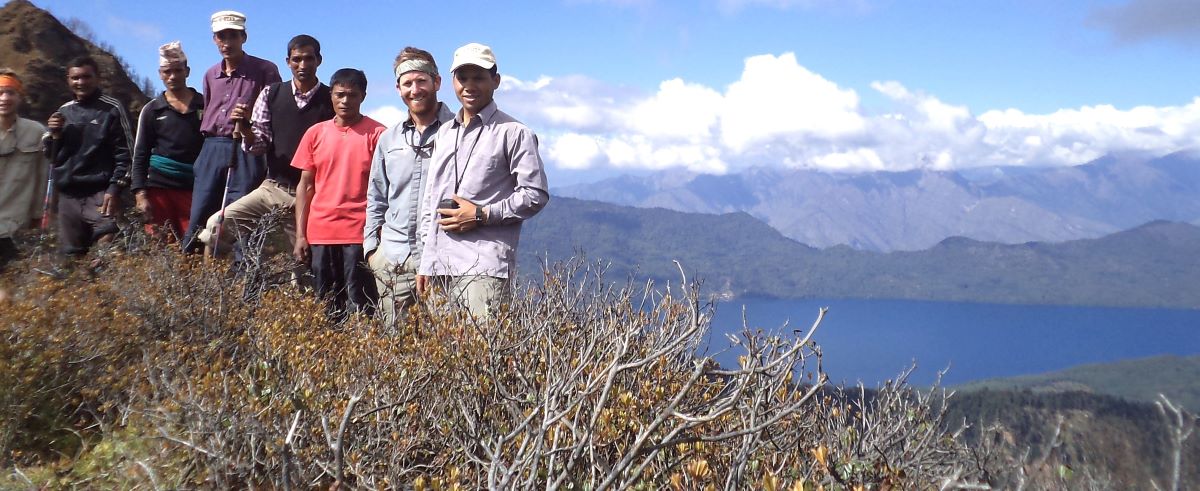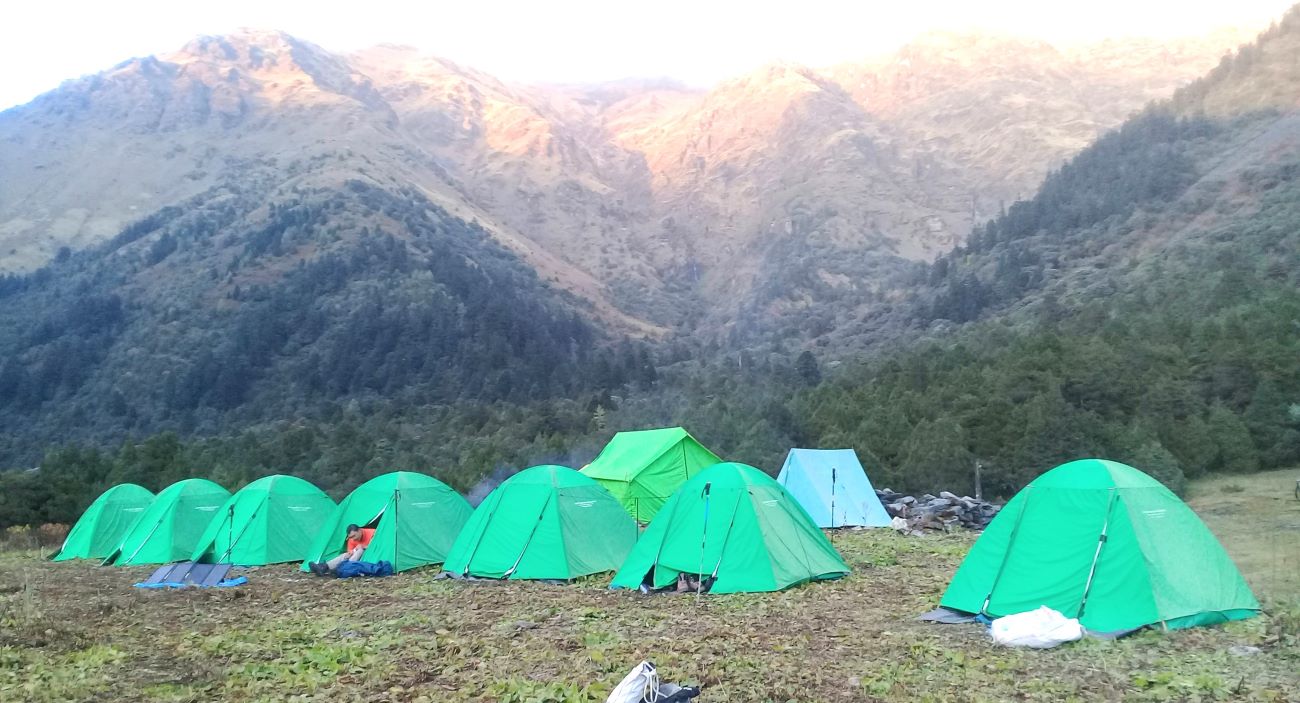
(Research on geoscience, anthropology, tourism…)
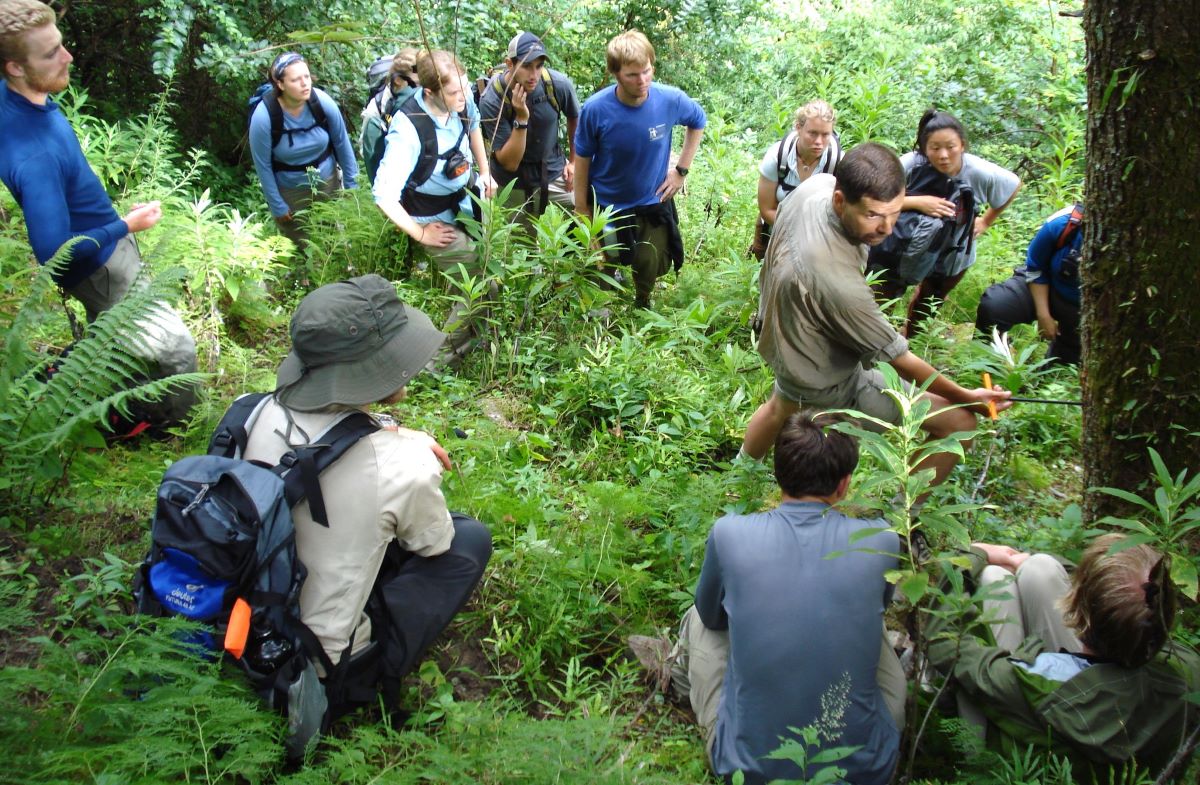
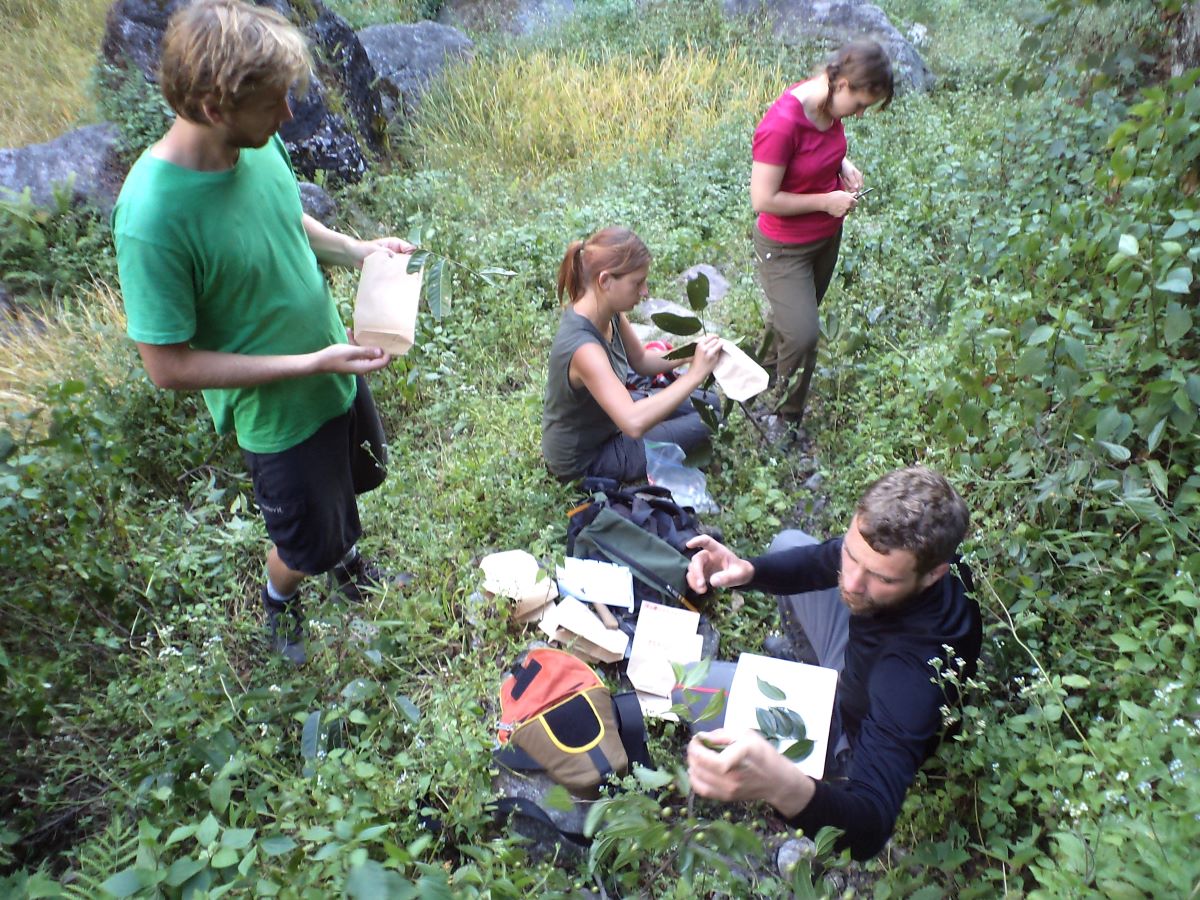
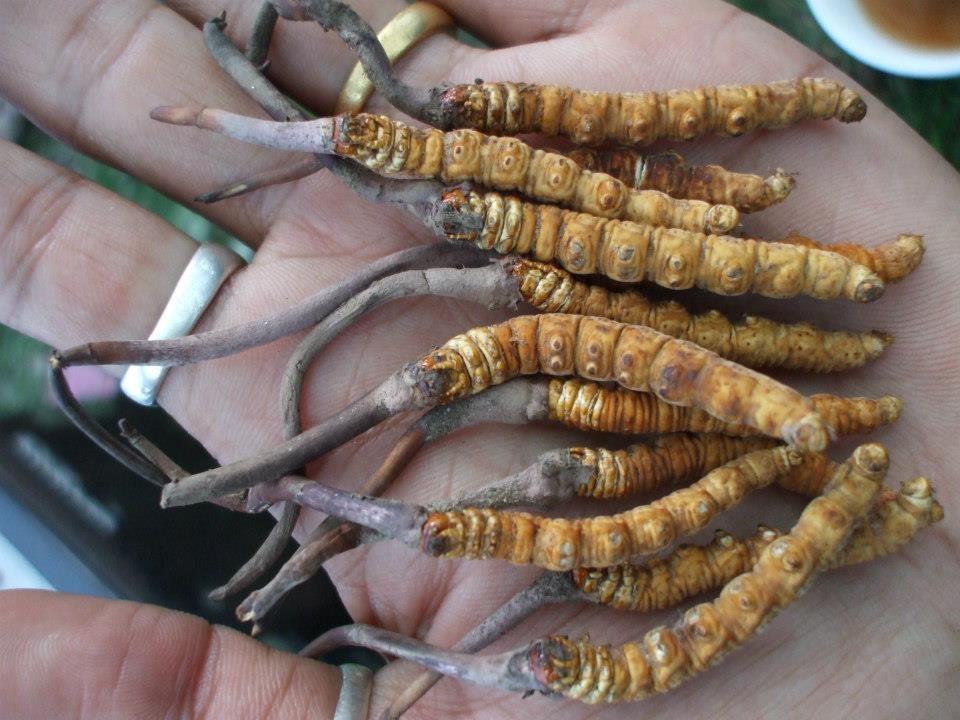
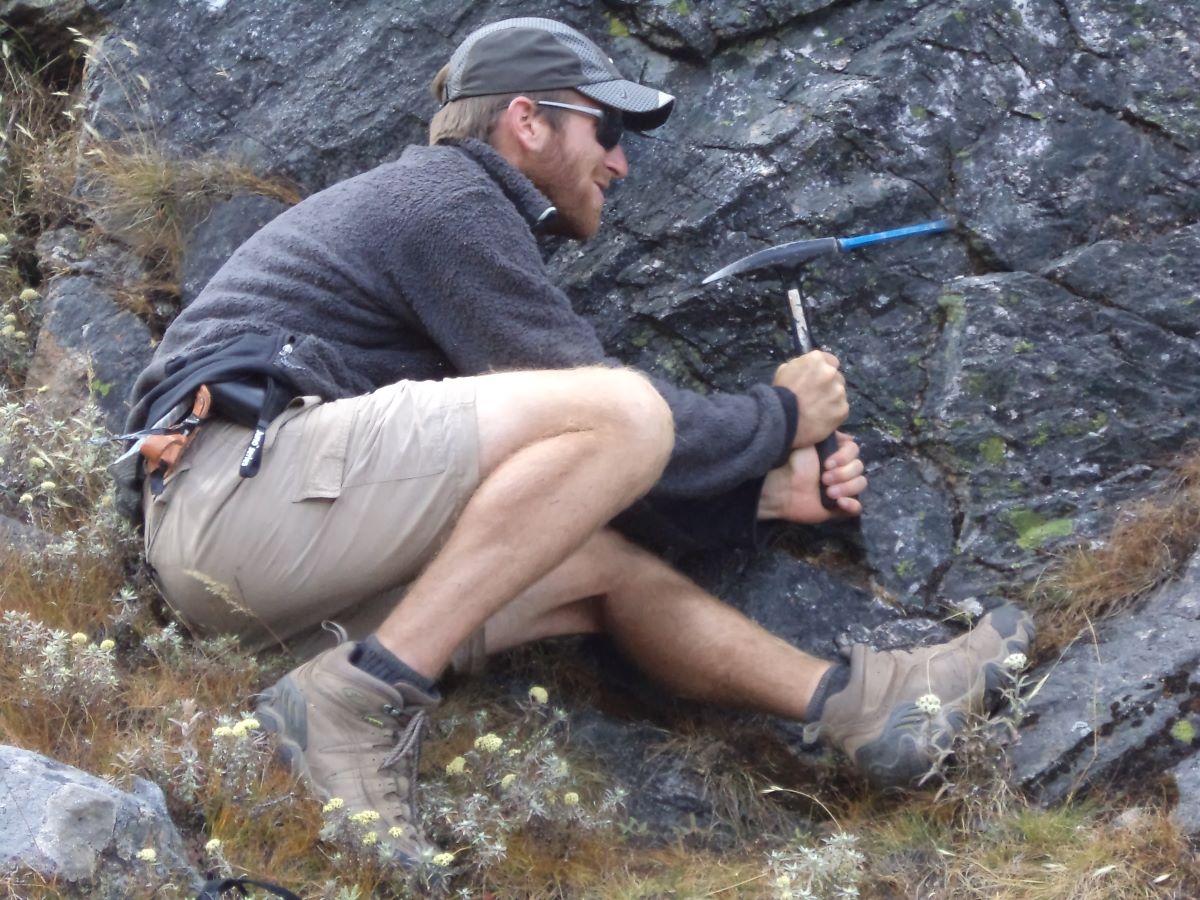
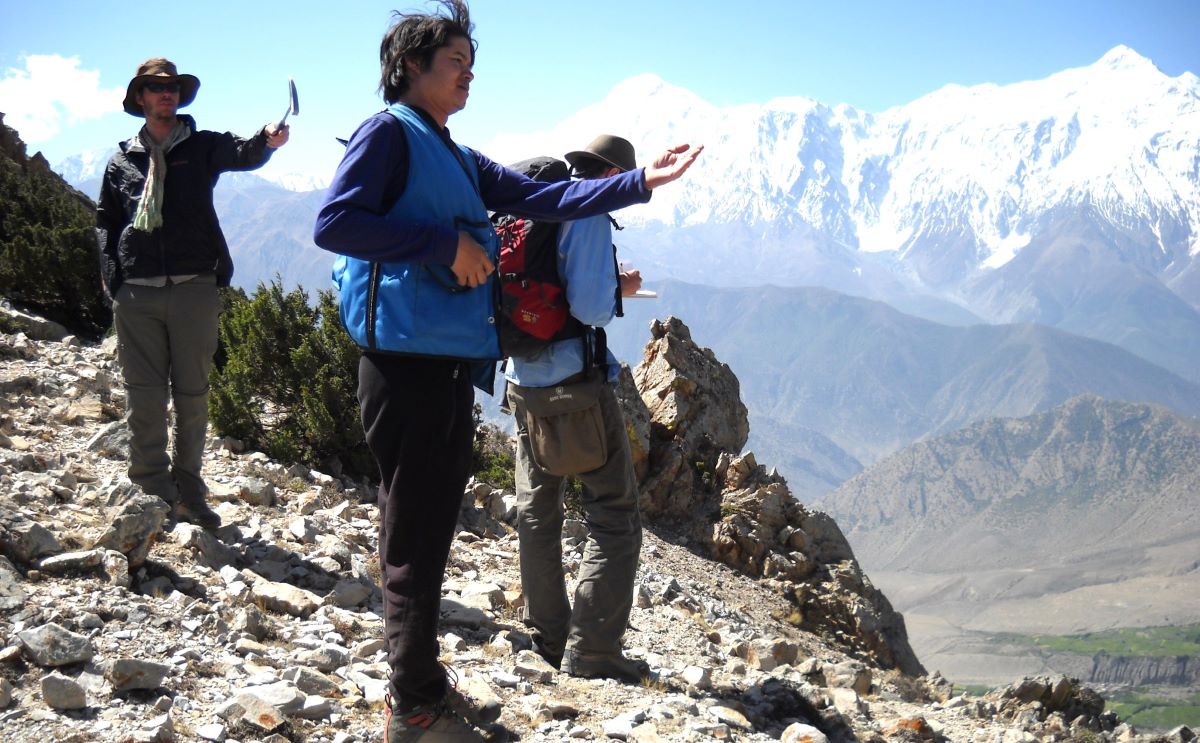
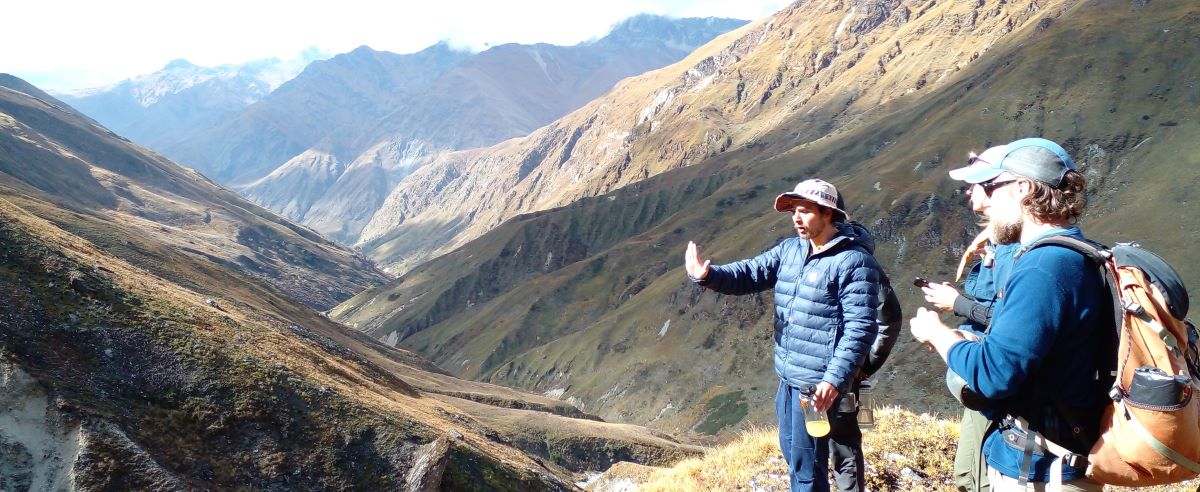
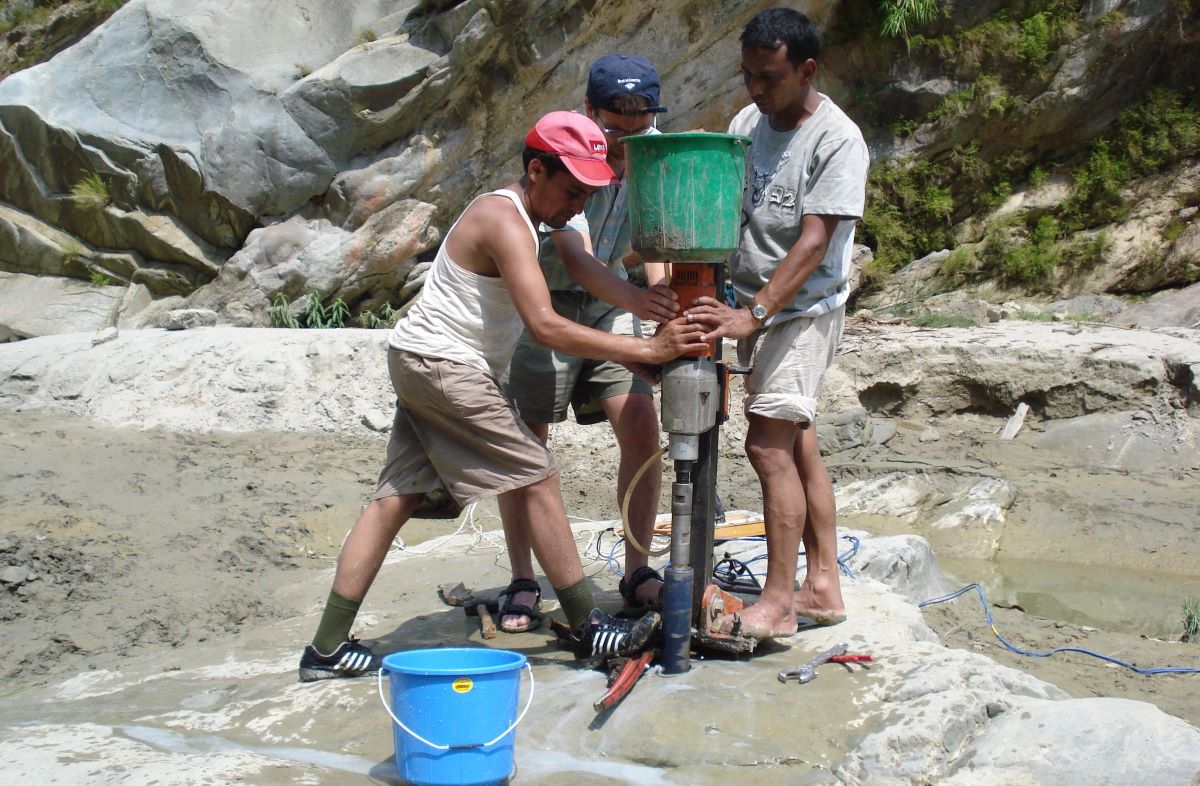
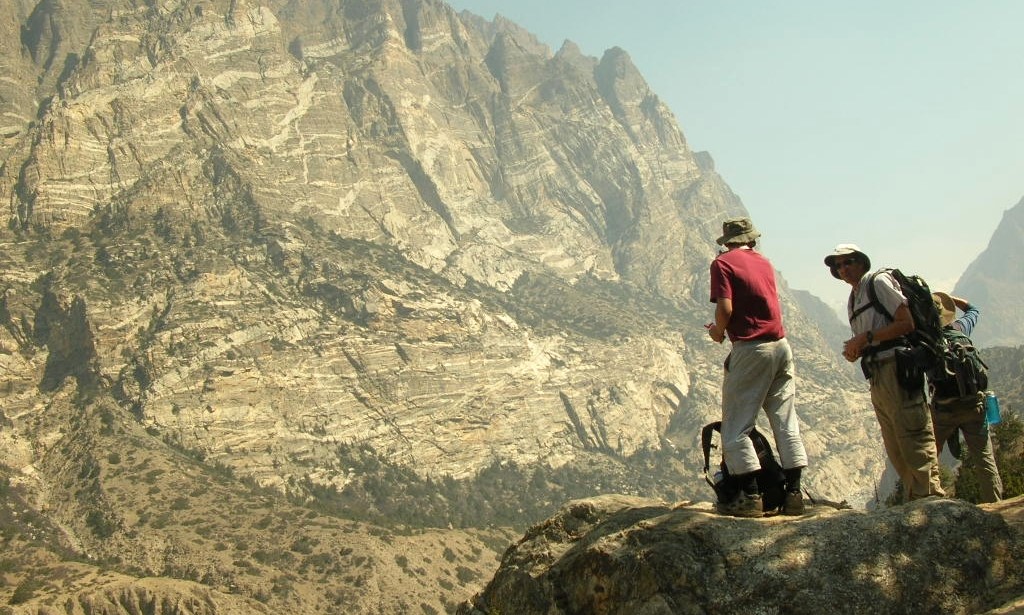
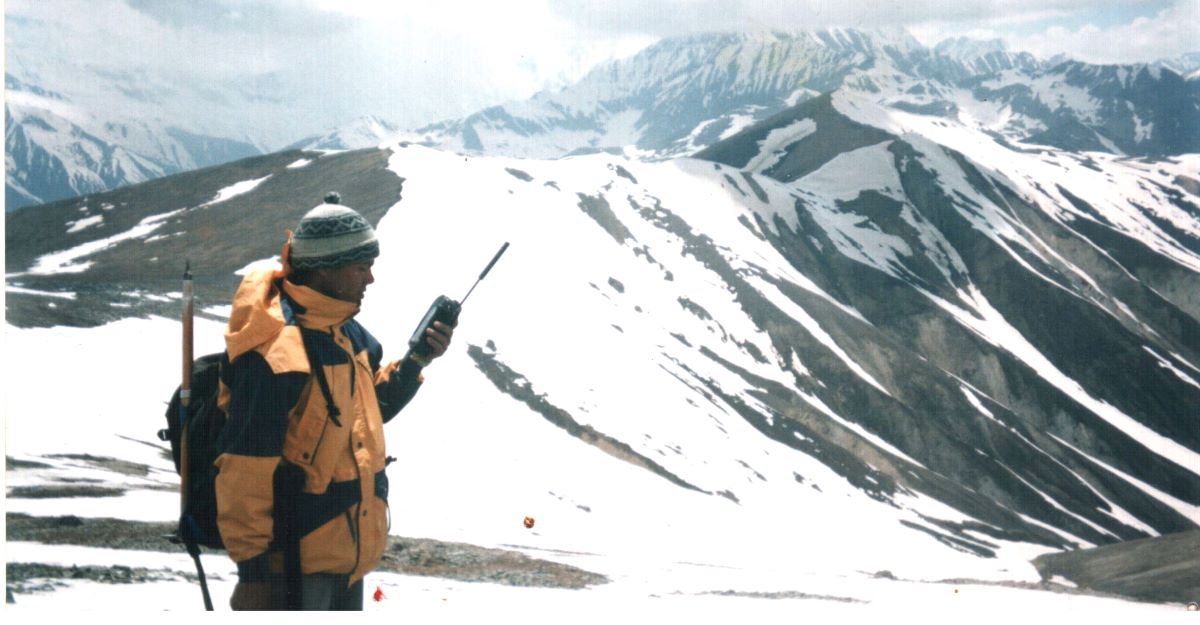
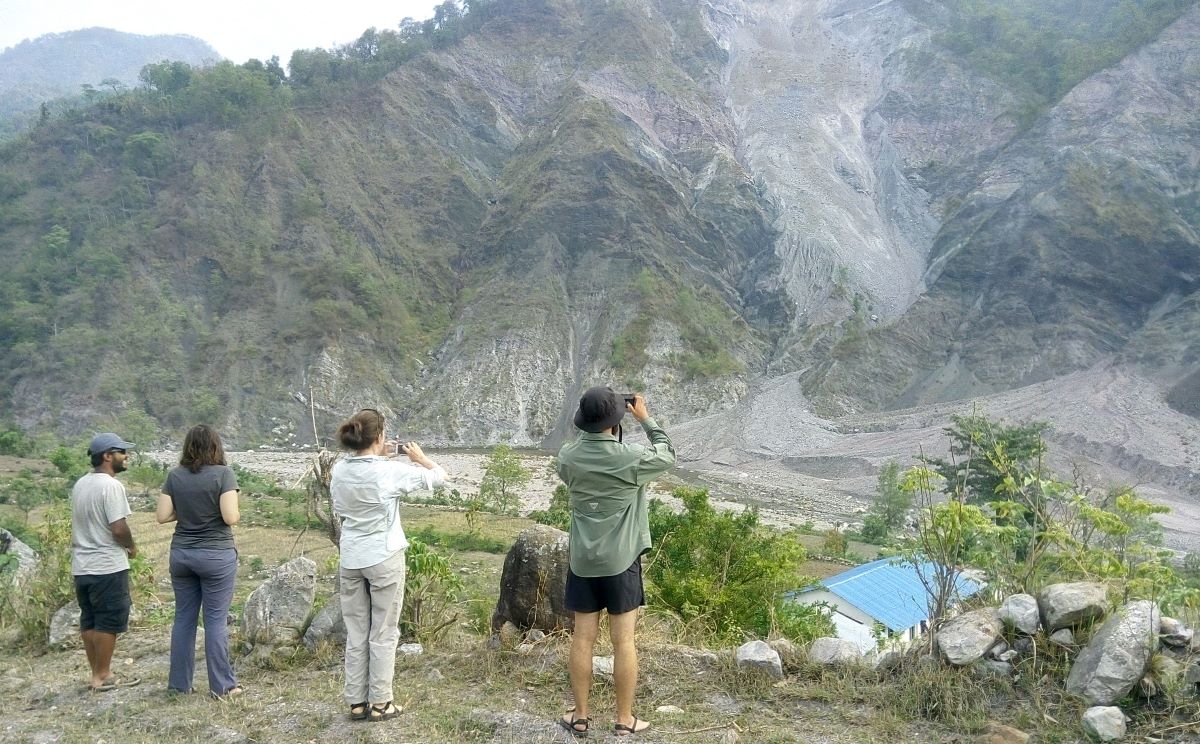
We have years of experience organizing field trips and project works where our guests can investigate and learn about Nepal's amazing geology, hydro-meteorology, anthropology, travel & tourism, photography & filming and many more.
This experience comes from many years of working with American and European earth scientists, anthropologists, trekkers, social scientists and tour operators. Our guides have organized logistical support and participated in research
trips and projects over the entire extent of Nepal and into adjacent areas of southern Tibet. We are supporting research projects ranging from modern-day climate studies to investigations of the Himalayan Fold Thrust Belt's major
faults as well as natural science and socio-economic- cultural aspects.
If you are interested in these fields of studies within Nepal, we can help make your research successful!
Most research projects in Nepal require official sanction from the government. We can facilitate all required paper work, including research permits from the government and even Parliamentary Memorandum of understanding (MOU).
We are able to provide a wide range of services (such as acquiring topographic maps, aerial photographs, biological and anthropological data etc) that will contribute to the success of any project.
The following major lithographic group of Nepal may help the geo-scientists for the region-wise and unit-wise study.
| Group | Age | Major Units | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siwalik group | Mid-Miocene to Pleistocene | Sand stone, mud-stone conglomerates | Siwaliks (east to west) |
| Coral group/Coral Thrust or MBT | Limestone, calcareous, shale | Siwaliks, eastern half of the middle mountain | |
| Nuwakot group | Precambrian to early Paleozoic | Arggillaceous with phyllites | Mountains |
| Katmandu group | Pre-Cambrian to Devonian | Katmandu group Pre-Cambrian to Devonian Schists, phyllites, marbles, quartzites, gneiss Middle mountains | Middle mountains |
| Himalayan gneiss group | Pre-Cambrian To Cambrian | Gneiss marble, quartzite | High mountains |
| Tethys or Tibetan group | Cambrian to Cretaceous | Dolomites, shale quartzite, sandstone | Himalayan region |
Centre for International Relations
Office of the Vice-chancellor
Tribhuvan University,
Kirtipur, Kathmandu.
4330840
Email: info.cir@tu.edu.np, director.cir@tu.edu.np
Proposal submission is a mandatory prerequisite for the foreign researcher who wants to conduct research work. In principle, the research proposal is an intellectual academic agreement between a researcher and the Centre for International Relations. The Centre reserves the right of approval or rejection of the proposal for further research. Summarizing the entire proposed work, the proposal should possess a considerable, noteworthy, pertinent outline that should be practicable to the supervisor. It is an outline of the entire research process that gives a summary of the information of the proposed research work. The main purpose of a research proposal is to show that the problem researcher proposes to investigate is significant enough to permit the investigation, the method planned to use by the researcher should be suitable and feasible. The expected outcome is likely to prove fruitful and will make an original contribution. A research proposal is also envisioned to convince others that the researcher has a worthwhile research project and have the competence and the work plan to complete it. In general, a research proposal should contain all the key rudiments involved in the research process and include sufficient information for the readers to evaluate the proposed study. The proposal resolves to help the researcher to focus and define their research plans. These plans are not binding, that may well change substantially as per the need of the progress in the research work.
Mange the margin of the page and the lines between the rows as per the sample page, (Font Name: Times New Roman, Font size for the Research Heading: 16, Font size for the subheadings: in between 14 & 12, Page Margin: Left: 1.5 inches and for all other sides: 1 inch as per the sample page. (See the page “Sample: 1” for reference.)
An abstract is a summary of the (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (6 -7 sentences, 150 - 250 words) long. A well-written abstract lets readers get the essence of the paper, follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in the full paper; and, help readers remember key points from your paper.
A Table of Contents is an organized listing of the chapters and major sections of the document. It is usually found on a page before the start of a written work, of its chapter or section titles or brief descriptions with their commencing page numbers. Readers will immediately be able to see how the manuscript is organized and then skip down to sections that are most relevant to them. A clear, concise, and well-formatted TOC is the first indicator of a good research paper.
This section should provide background information related to the proposed research heading and the context of the study. It may start with or include geographical, historical, cultural, political, social or organizational information about the context of the proposed research and may also include a theoretical starting point and policy of the research.
This section must include the issue that exists in practice, in the literature or in the theory which leads to signify the need for study of the proposed topic.
Put forward a clear and concise statement about the objective/purpose/aim of the research. Briefly outline and demarcate the specific area of the research. Identify and define the fundamental notions or designs of the research work.
A review of literature provides an overview of the current research comprising a survey of scholarly sources of available data and knowledge. Therefore, in this section, the researcher must produce a review of significant writers/researchers in the field proposed topic or proposed area of study. The sources include books, journal articles, and newspapers related to the research question of the proposed research. Moreover, it summarizes, analyzes, interprets, and evaluates the relevant theories, methods, points of view, and gaps in the existing literature. If a proposed area of research is new or undone previously, the researcher may present discussions on the research question and its various aspects of the relevant study to support the claim. An approach of critical inquiry will be more appropriate to show the researcher’s prudence and awareness in the selection of the topic to the supervisor and the department. The length of a literature review usually depends on the length of the research project. For example, if you are writing a research paper of 10 pages. You will have to include 5 to 6 sources in your literature review.
i) Conceptual Framework: For showing the relationships between different ideas to relate them in the research study describe the conceptual framework of the proposed research. It is a commonly used organized way to visually explain the systems, relationships, concepts, and ideas of the proposed research. It can be in narrative form or a graphical form, showcasing the key variables or constructs and the present relationship.
ii) Research Design: Research design refers to the overall strategy that has to be chosen to incorporate the different components of the study coherently and logically to ensure the researcher will effectively address the research problem. It is the framework of research methods and techniques chosen by a researcher. The design allows researchers to refine research methods suitable for the subject matter and set up their studies for success. Research design constitutes the blueprint for the collection, measurement, and analysis of data.
iii) Nature & Sources of Data: In this section mention that the proposed research work will be based on secondary or primary data (i.e. nature of the data). Moreover, also clarify the sources of data whether it is statistical or non-statistical. The Statistical sources refer to data gathered for official purposes, incorporate censuses, and officially administered surveys. Non-statistical sources refer to the collection of data for other administrative purposes or the private sector.
iv) Sampling Strategy: Choosing an appropriate sampling strategy as per the design of the proposed research including qualitative or quantitative research is an essential step in the capture phase of the data journey. It will ensure the reliability of the collected data and reflects the characteristics of your target group. Followings are the major steps of choosing the sampling strategy:
Step 1: Define sample and target population as per the objective of the proposed research.
Step 2: Define the sample and target population,
Step 3: Define sampling technique,
Step 4: Minimize the sampling error.
v) Methods and Instruments of Data Collection: Instruments: Instruments of Data collection refer to the devices or instruments used to collect data, such as Computer-assisted Interviews, Direct or Indirect Personal Interviews, Telephonic Interviews, Case studies, Checklists, Observations, Surveys and Questionnaires tools are used to collect data. Data collection Method: Data collection is a process of gathering information from all the relevant sources to find a solution to the research problem. It helps to evaluate the outcome of the problem. Depending on the types of data the data collection method is divided into two categories:
A. Primary Data Collection Method
Primary data or raw data is a type of information that is obtained directly from the first-hand source through experiments, surveys, or observations. This method is further classified as:
a) Quantitative Data Collection Methods :
i) Observation Method :
ii) Interview Method :
iii) Questionnaire Method
iv) Schedule
B) Secondary Data Collection Method
Primary data or raw data is a type of information that is obtained directly from the first-hand source through experiments, surveys, or observations. This method is further classified as:
i) Government publications
ii) Public records
iii) Historical and statistical documents
iv) Business documents
v) Technical and Trade journals
i) Diaries
ii) Letters
iii) Unpublished biographies etc.
b) Qualitative Data Collection Methods
i) Interviews: Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
ii) Focus groups: Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
iii) Ethnography: Participating in a community or organization for an extended period to closely observe culture and behaviour.
iv) Literature review: Survey of published works by other authors.
Method of Analysis: Methods of data analysis comprise certain tools that the researcher can use to analyze data. Mainly there are two main categories - qualitative and quantitative data analysis. Since there are different types of data analysis methods and tools available choice of the tool depends on the type of data and the objective that the researcher wants to achieve with it. If the data is quantitative, then the researcher should choose the quantitative method. Otherwise, the qualitative method should be chosen. For quantitative analysis, tools like average, mean, mode, median, frequency, range, regression, correlation, and variance are available. In the case of qualitative analysis, tools like content analysis, narrative analysis, discourse analysis, and grounded theory are available to analyze the data. Different types of data require different methods of data analysis. A poorly chosen method will endanger the authenticity of the research and leads to wrong results. Therefore, the researcher must carefully choose the correct method of data analysis.
Significance or Importance or Rationale of Study indicates the value addition of the research work. It should be wrapped with the existing level of knowledge and the expected outcome. This section should indicate how the research work proposed to carry out will significantly upgrade or upkeep to extend the existing level of knowledge and practice in the area of research.
Research work plan like other plans, keeps the researchers organized while doing the research. It may be written stepwise, in sections, or phases. Detail the procedure and experimental design that will be used. It may be presented in the form of diagrams or flow charts, tables, etc.
A research proposal budget plan is often written in a linear or tabular format and it details all the expenses which are connected with the proposal project. (Note: All expenses incurred in the research work should be funded by the researcher personally. Salaries, wages and VISA Fees must comply with the budget.) (“Sample: 2” for reference).
References follow the text in a section headed REFERENCES (use first-level head format identified earlier).
· All references should be double-spaced and use a hanging indent.
· All references should be in alphabetical order by first authors’ last names.
(Manage double space between the lines of the title and type the title in inverted pyramid form)
Vice-Chancellor’s Office Building Tribhuvan University,
Kirtipur, Kathmandu, Nepal,
Submitted by:
Contact Number:
Passport Number:
(Manage double space between the lines of the title and type the title in inverted pyramid form)
| S. No. | Category | Monthly Expenses | Total Project Expenses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lodging Expenses | ||
| 2 | Travel Expenses | ||
| 3 | Research Assistant Expenses | ||
| 4 | Research Materials Expenses | ||
| 5 | Communication Expenses | ||
| 6 | Data Processing /Printing / Royalty | ||
| 7 | Supervision Expenses | ||
Total Expenses |






































































